Multi-Objective Planning in Stochastic Ocean Environments
This work was published in MDPI Journal of Marine Science and Engineering: GPU-Accelerated Multi-Objective Optimal Planning in Stochastic Dynamic Environments.
The importance of autonomous marine vehicles is increasing in a wide range of ocean science and engineering applications. Multi-objective optimization, where trade-offs between multiple conflicting objectives are achieved (such as minimizing expected mission time, energy consumption, and environmental energy harvesting), is crucial for planning optimal routes in stochastic dynamic ocean environments. This work extends the end-to-end GPU-accelerated single-objective Markov Decision Process path planner to compute optimal operating curves for multi-objective optimal planning. MDPs with scalarized rewards for multiple objectives are formulated and solved in idealized stochastic dynamic ocean environments with dynamic obstacles. Two simulated mission scenarios are completed to elucidate our approach and capabilities: (i) an agent moving from a start to target by minimizing travel time and net-energy consumption when harvesting solar energy in an uncertain flow; (ii) an agent attempting to cross a shipping channel with uncertain ship movement and flow. Optimal operating curves are computed in a fraction of the time that would be required for existing solvers and algorithms.
Contributions
Multi-objective Rewards: Utilizing a finite horizon, undiscounted, total cost MDP, I devised scalarised multi-objective reward function using weighted rewards for energy comsumption and required time. Solar energy harvested from a scalar field can also be accomodated to optimize net consumption. The GPU-accelerated algorithm was implemented on CUDA.

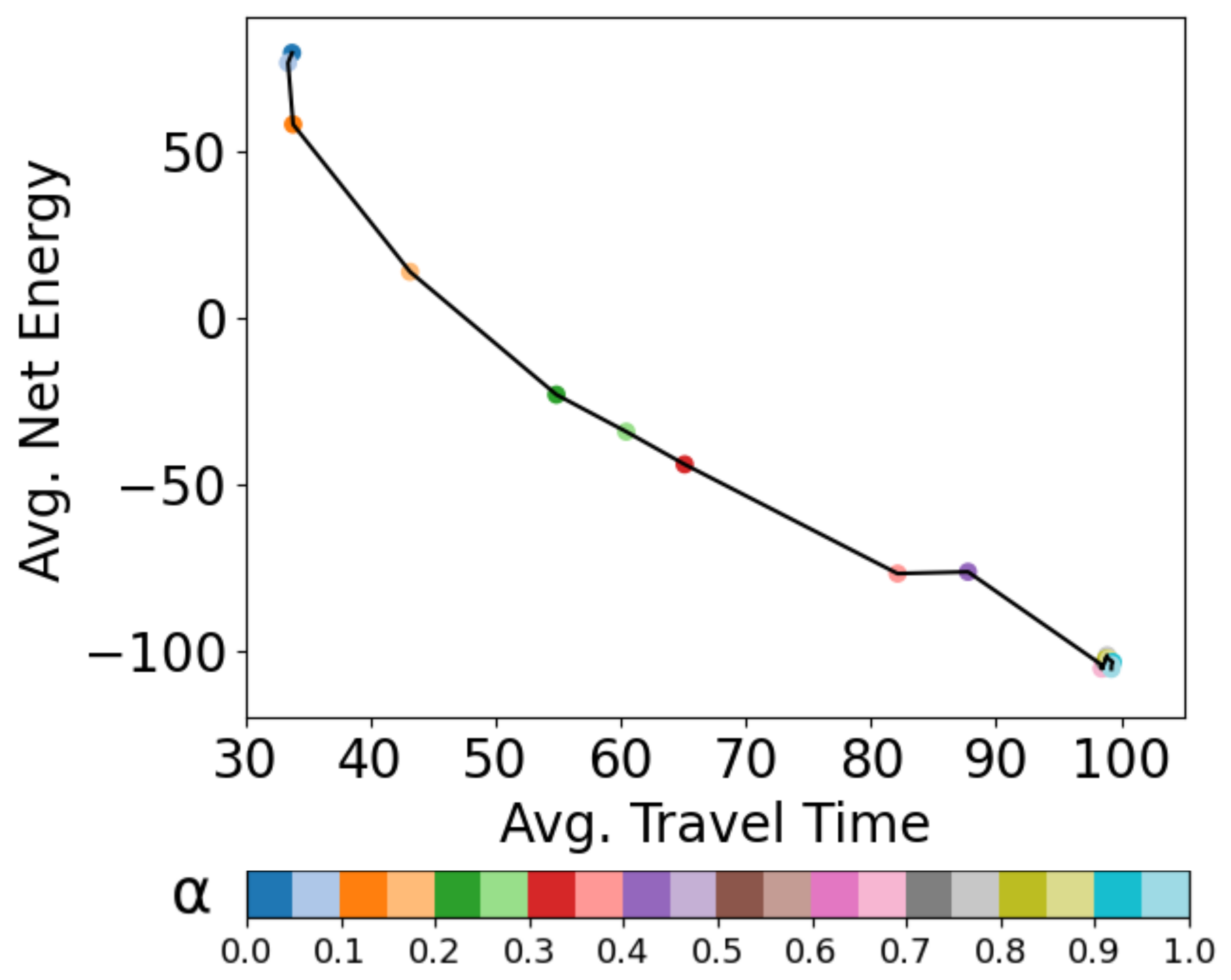
Operating Curve Analysis and Applications: I analysed the operating curves for various problem parameters, showing several interesting characteristics and agent behaviors. It developed further applications on unknown obstacle positions and busy shipping channel crossing problem.
